A preposition comes before a noun or a pronoun to show place, time, direction, etc.

Prepositions
We use the “preposition of time” when we talk about time. It answers the question of (When). Three very common prepositions before (earlier than) after (following in time; later than) for (used to show a length of time) since (from a time in the past until now) by (before or not later than) during (while, throughout) until/till (up to, no longer than)
Preposition of time
at
on
in
precise time
days and dates
long periods, time period
at the moment
on Sunday
in 2 minutes
at 2 o’clock
on Monday morning
in three hours
at dinnertime
on June 12
in June
at noon
on my birthday
in summer
at sunrise
on our anniversary
in 2012
at night
on the first day
in the 70s
at the end
on the last day
in the past
More time prepositions.
We use the “preposition of place” when we talk about the location of things or people. It answers the question of (where). Three very common prepositions above (in or to a higher place than) across (on the other side of) among (in the middle of) behind (at the back/rear of) below (in a lower position) beside (at the side of) between (in the middle of two things, people, or places) by (at the side of) near (close to; a short distance from) under (beneath, below)
Preposition of Place
at
on
in
specific point or place
surface
enclosed space or space with boundaries
at the door
on the page
in the book
at the bus stop
on the menu
in my pocket
at the station
on the table
in the elevator
at the corner
on the roof
in the car
at home
on the wall
in the swimming pool
at work
on the ceiling
in Paris
at the cinema
on the floor
in America
More place prepositions
We use the “prepositions of movement” when we talk about movement from one place to another, and they often come after verbs of motion. They are also called the prepositions of direction. More examples
Preposition of movement
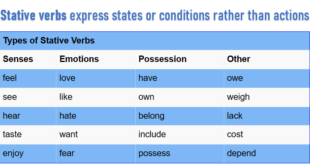
The “preposition of agent and instrument” describes a person or thing that is the cause of something occurring. The “preposition of manner” describes the way or means by which something happens. It answers the question of (how) The “Preposition of Possession” shows ownership. We use the “preposition of contrast” when we link two contrasting ideas. Some prepositions are more than one word.
More prepositions